11.1. Type of protection “n” – non incendive
EMMUA 214 States: Page 18
3.5.1 Definition A type of protection applied to electrical equipment such that, in normal operation and in certain specified abnormal conditions, it is not capable of igniting a surrounding explosive atmosphere.
Note 1: Additionally, the requirements of IEC 60079-15 are intended to ensure that a fault capable of causing ignition is not likely to occur.
Note 2: An example of a specified abnormal condition is a luminaire with failed lamp.
3.5.2 Standards and selection
i) Current standards
IEC 60079-15 (EN 60079-15) Explosive atmospheres Equipment protection by type of protection ‘n’.
ii) Superseded standards
EN 50021 Type of protection ‘n’;
BS 4137 Guide to the selection of electrical equipment for use in division 2 areas; and
BS 6941 Electrical apparatus for explosive atmospheres with type of protection N
iii) EPL/category and zone of use
Equipment may only be used in areas requiring EPL ‘Gc’ or Category 3. Prior to 2007 it was restricted to use in Zone 2 only.
iv) Use with gas subdivisions
Equipment would have been designed for use either gas in Group Il or with a particular Group Il gas subdivision. It would be marked either with Il or with IIA, 11B, or IIC. The marking did not include the subdivision if it was suitable for all subdivisions, just Il followed by other required details.
Recently IEC has dropped the Group Il marking and requires equipment to be marked IIA, 11B or IIC.
3.5.3 Construction and use
Ex ‘n’ is subdivided into a number of types:
Type A: non-sparking (has been replaced by Ex ‘ec’)
Type R: restricted breathing enclosure;
Type L: energy limited equipment (has been replaced by Ex ‘ic’);
Type Z: enclosure with ‘n’ pressurisation (has been replaced by Ex ‘pz’ );
Type C: sparking where the contacts are suitably protected other than by type R, L or Z.
Hermetically Sealed Device Type C
Sparking contacts may be safely enclosed within a hermetically sealed enclosure. The seal may be by soldering, brazing, welding or the fusion of glass to metal.
Enclosed Break Devices Type C
A type ‘n’ enclosed break device incorporates electrical contacts. It is able to safely withstand an internal explosion of any flammable gas that may have entered inside.
Encapsulated Device Type C
An encapsulated device has similarities with a hermetically sealed device. Externai connections are normally by flying leads or terminals.
Restricted Breathing Type R
Where an enclosure is designed to restrict, but not totally prevent, the entry of gases. The vast majority of applications are with luminaires. The positioning of restricted breathing enclosures may need to be carefully considered, particularly in open sunlight. Manufacturer’s instructions should be adhered to (e.g. cab}e entry requirements incorporating the correct IP washer, periodic testing of restricted breathing properties and replacement of gasket seals when relamping).
v) Energy Limitation - Type L
Where circuit components restrict the maximum available energy in an external circuit to a level incapable of causing gas ignition. Ex’nL’ has been replaced by Ex’ic’.
Apparatus designed so that in normal operation is not capable of igniting a surrounding explosive atmosphere.
A fault capable of causing ignition is not likely to occur.
Protection method only suitable for use in Zone 2 areas under normal conditions.
It is a protection method mainly used in the UK but with ATEX Directives the concept has been enforced in the European community.
Certification conformity is recorded as Ex N (UK) or Ex n (ATEX).
Type N or n items are surface industry, gas group II only, sometimes are sub divided IIA, IIB and IIC.
Temperature class must be taken into account.
Since the design requirements are not as strict as those for increased safety type ‘e’ protection, it is possible for the manufacturer to install within type ‘n’ apparatus, components which produce hot surfaces, arcs or sparks, providing these components have in them additional methods of protection.
The principal design features for type ‘n’ apparatus are as follows:
- Enclosures and motor fan guards, where exposed to high risk of mechanical damage, to have resistance to impact
- Minimum ingress protection IP54 where an enclosure has internally exposed live parts
- Use of certified terminals
- Terminals manufactured form high quality insulation material
- Specified creepage and clearance distances incorporated into the design of the terminals
- Terminal locking devices to ensure conductors remain secure in service
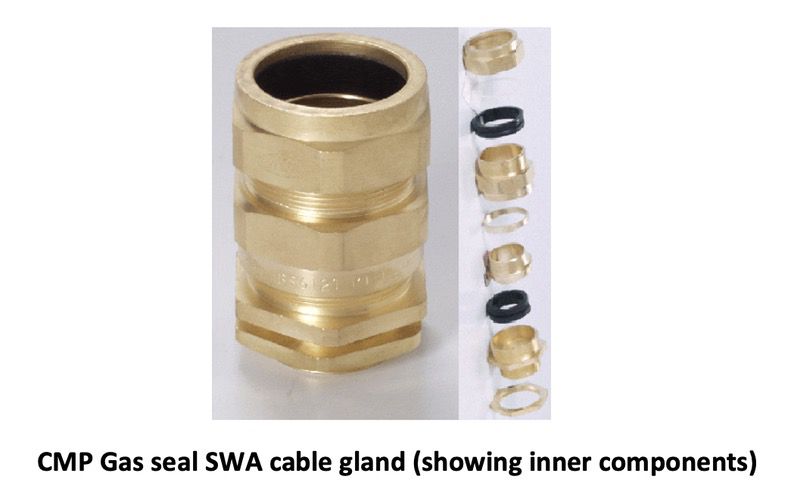

11.1.1. Installation of Ex n Equipment
Exn equipment is used where a lower risk level of explosive atmosphere is present.
- Enclosures and terminals are made to good engineering standards.
- Cable requirements are reduced but wire protection is required to prevent damage from sharp edges and crimping in moving parts.
- Cable insulation must withstand a test of 500 volts up to 90volts operating, and 1000/1500 volt test for higher operating voltages.
- Glands need to be certified.
- A threaded entry of 6mm or more will maintain IP54 protection
- Less than 6mm wall thickness, a sealing washer is required
- The gland must maintain IP54 degree of protection
1.1.1. Common Use of Type Ex n Apparatus
Electrical items such as:
- Motors
- Light fittings
- Push buttons
- Junction boxes
Instrument items such as:
- Solenoid valves
- Transducers
- Electronic equipment, where voltages are kept low; typically below 60Va.c, 75Vdc
Equipment that can produce arcs, sparks and hot surfaces must satisfy the following conditions:
- An enclosed break device
- Non-incendive component
- Sealed device
- Hermetically (air tight) sealed device
- Encapsulated device
- Energy limiting apparatus or circuit
- Restricting breathing in hot surface conditions
1.1.2. Light Fittings
Light fittings can use most types of lamp, except for those containing sodium in vapour or metallic form. Lamps, which use a starter switch, must use a switch that is hermetically sealed. Lamps cannot be change while fitting is live with electrical power. A notice to remove power before opening the light enclosure must be displayed.
1.1.3. Rotating Machines
Rotating parts should be designed that there is sufficient mechanical clearance between parts so as not to spark or heat up. No guidance on clearance dimension is given. If the machine has a repetitive operation then temperature rise at start-up needs to be considered with respect to T classification. Normal start-up condition is not seen as problem.
1.1.4. Non Incendive Ex nL
Energy limited apparatus and circuits achieve safety by ensuring voltages and currents are maintained at safe levels, which is now covered by I.S. protection Ex i c (section 16) but you may come across this on older equipment.
11.1.6. Energy limited apparatus
Apparatus of this type containing normally sparking contacts, on its own, and suitable for use in a hazardous area, is required to be marked ‘Apparatus containing energy-limited circuits’.
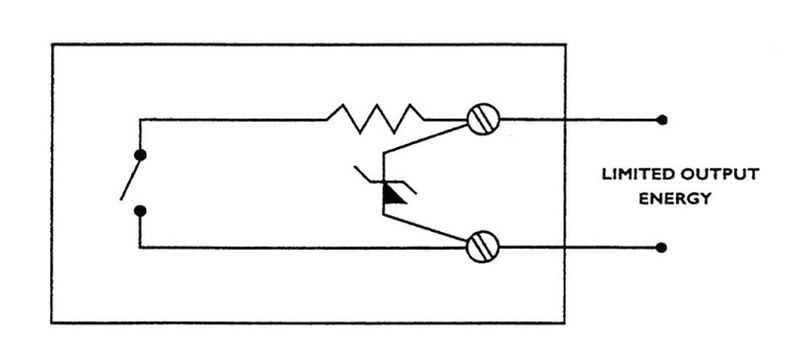
Methods employed to limit voltage and current in this type of apparatus will include the use of zener diodes and series resistors etc.
11.1.7. Energy limited circuits
The assessment for this type of apparatus, which contains normally sparking contacts, considers external influences such as inductance or capacitance of cables or connected apparatus. The apparatus must be marked ‘Apparatus for connection to energy-limited circuits’.
These installation conditions will be specified in the certificate documentation to enable safe installation of the apparatus.